Check Free Memory Slots Linux
Here’s a useful way of finding out how many memory slots are occupied on the motherboard of a machine without removing the cover, as well as how much installed physical memory is supported.
Check Free Memory Slots Linux Also, you should note that there is a search function which you can use to locate specific Check Free Memory Slots Linux games. Some notable roulette games which you can play Check Free Memory Slots Linux on the platform are Lightning Roulette, Immersive Roulette, Auto Roulette, and Speed Roulette Live. The number of memory devices in the results of sudo dmidecode -type 17 is equal to the number of memory slots, so the command to print the number of RAM slots is: sudo dmidecode -type 17 grep 'Memory Device' -count The results of this command will be one integer number equal to the number of RAM slots.
By far the easiest way to check the number of RAM slots currently in use in your machine without opening it up is to use the DMI Table Decoder command called dmidecode, which gives you a flat report. At the command prompt, type sudo dmidecode -t 16 and push enter. You’ll probably be asked for your administrator password. 10 Free Tools To Optimize RAM Memory For Windows And macOS. 10 Free Screen Capturing Tools For Windows, Mac & Linux. 13 Free Tools To Create Bootable USB Windows 10 & Linux With ISO Files. 8 Free GPU Video Card Test Tools – Check Memory Errors & Overclocking Stability. A quick way to check memory slots on a Linux box July 19, 2012 Leave a comment Here’s a useful way of finding out how many memory slots are occupied on the motherboard of a machine without removing the cover, as well as how much installed physical memory is supported.
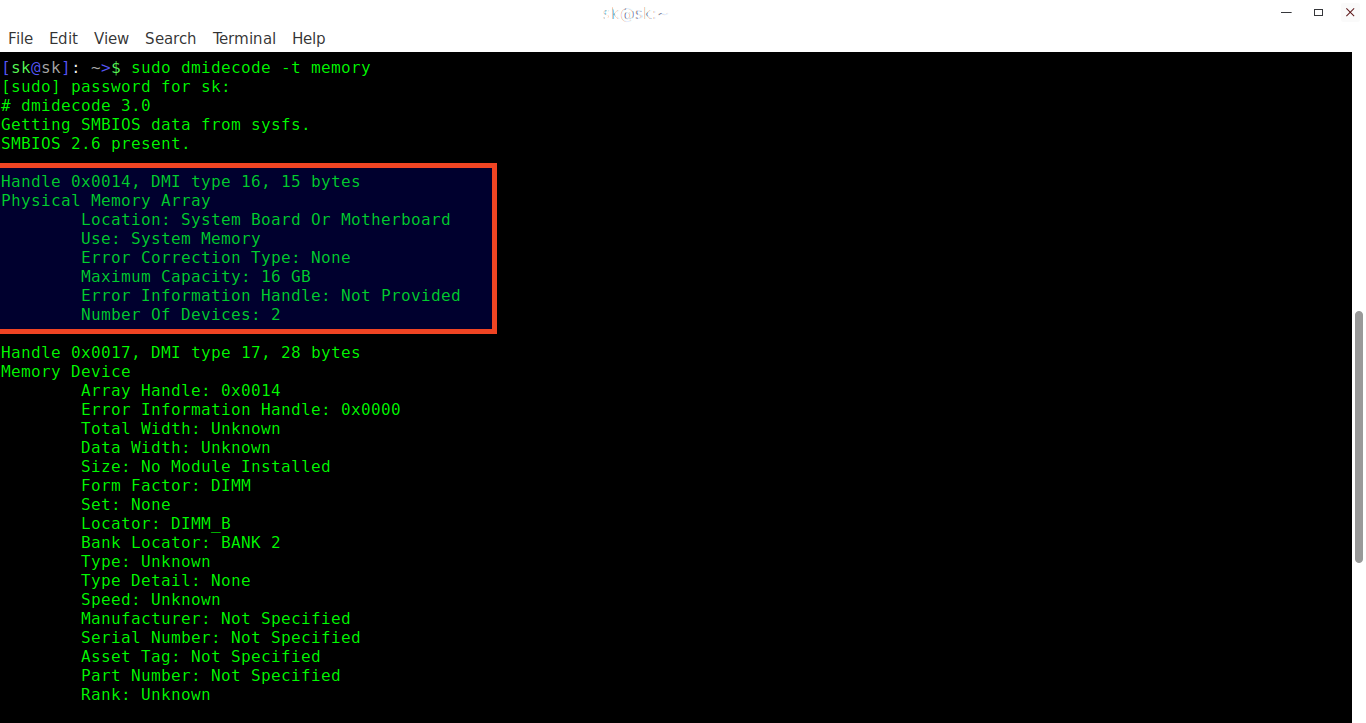
We can use the dmidecode command to reveal your systems DMI table, which contains details of the systems hardware.
Check Free Memory Slots Linux Software
There are a whole load of DMI types we can look at – a full table of those at the end of this article.
In this particular case, we are interested in memory – type 16 ‘Physical Memory Array’ will show us how much memory is supported and DMI type 17 will reveal details of currently installed memory.
So, first off:-
dmidecode -t 16
Maximum Capacity shows us the maximum amount of memory can be installed in the machine. Number of devices tells us how many slots there are on the motherboard – in this case, 8.
Now we can interrogotate DMI type 17 – ‘Memory Device’ to show us details of installed memory

dmidecode -t 17
Each module installed will be listed with the the information given above. If we just want to know how many modules are installed and what size they are, we only really need the Size: – so we use grep
dmidecode -t 17 grep Size
From this we can see that 8x 2048MB modules are installed – so all the slots on the motherboard are populated.
There is plenty of other useful information that can be retrieved using dmidecode, including
-t1 System
-t2 Base Board
Check Free Memory Slots Linux Mint
-t3 Chassis
Check Free Memory Slots Linux Downloads
-t4 CPU
-t9 PCI slots
Check Free Memory Slots Linux Download
Full SMIBIOS Specification
Check Free Memory Slots Linux
1 System
2 Base Board
3 Chassis
4 Processor
5 Memory Controller
6 Memory Module
7 Cache
8 Port Connector
9 System Slots
10 On Board Devices
11 OEM Strings
12 System Configuration Options
13 BIOS Language
14 Group Associations
15 System Event Log
16 Physical Memory Array
17 Memory Device
18 32-bit Memory Error
19 Memory Array Mapped Address
20 Memory Device Mapped Address
21 Built-in Pointing Device
22 Portable Battery
23 System Reset
24 Hardware Security
25 System Power Controls
26 Voltage Probe
27 Cooling Device
28 Temperature Probe
29 Electrical Current Probe
30 Out-of-band Remote Access
31 Boot Integrity Services
32 System Boot
33 64-bit Memory Error
34 Management Device
35 Management Device Component
36 Management Device Threshold Data
37 Memory Channel
38 IPMI Device
39 Power Supply
40 Additional Information
41 Onboard Device